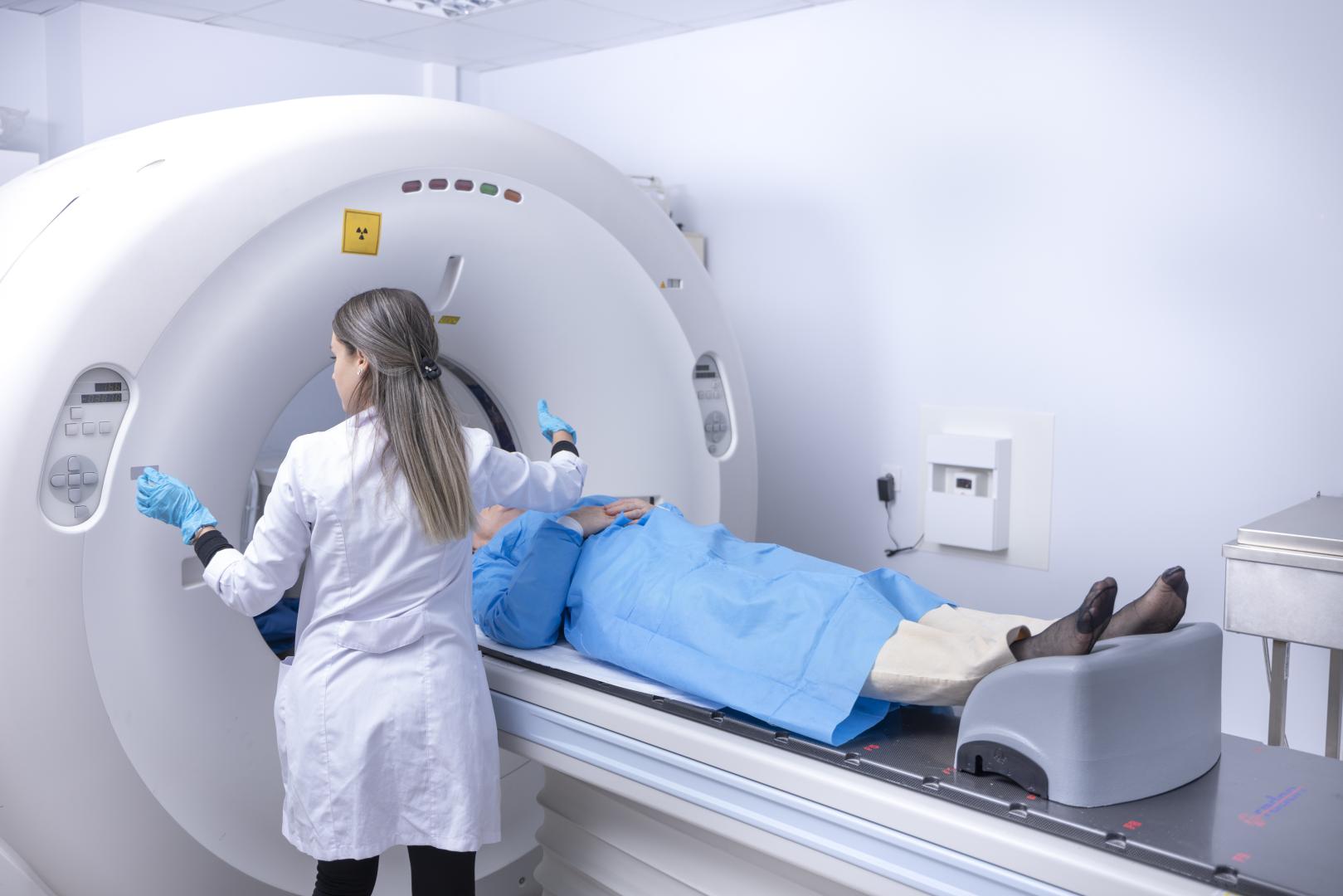
No-cost Cancer Screenings
You may be eligible for a no cost lung cancer screening:
- Are you age 50 – 80; and,
- Do you have a > 20 pack-year smoking history; and,
- Do you currently smoke or have you quit smoking in the past 15 years?
If you answered yes to one or more of these questions, call 410-222-6180 or 410-222-6071 (Spanish) to learn more about how to get screened for lung cancer.
Funded by the Cigarette Restitution Fund
Benefits of Quitting Tobacco
There are many health benefits when you quit smoking no matter what age you are. In just 20 minutes, the body can start to benefit from quitting. Here are ways quitting smoking can improve the body.
BRAIN
Quitting will help the nicotine receptors in the brain become normal and help stop addiction.
HEART
When you quit smoking, the risk of heart attacks decreases. Quitting can lower blood pressure and heart rate within 20 minutes. In a year, the added risk of coronary heart disease is now half that of a smoker.
Quitting can lower cholesterol levels and fat circulation in the body.
LUNG
Within 1 to 9 months, individuals can find it easier to walk up the stairs without shortness of breath.
The cilia, which help keep airways clear in the lungs, regrow and regain normal function. When the cilia work properly, the body can fight off colds and infections.
FACE and HEAD
Sharper Hearing: Quitting will help sharpen your hearing.
Clearer Vision: Overall vision will improve, and quitting can stop the damage that smoking can do to your eyes.
Clean Mouth: After a few days without cigarettes, your smile will be brighter. The risk of tooth loss decreases and your breath smells better.
Clearer Skin: Quitting can help clear blemishes and protect the skin from premature aging and wrinkles.
STOMACH
Quitting can reduce belly fat and lower the risk of diabetes. If you already have diabetes, quitting can help you have better control of your blood sugar levels.
Don’t wait, quit smoking TODAY!
Lung Cancer Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is the presence of cancer cells in the tissues of the lungs, usually in the cells lining air passages. There are two types of lung cancer. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is most common and grows and spreads slowly. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) grows and spreads faster than NSCLC.
What are the Risk Factors for Lung Cancer?
Research has shown that people with certain risk factors are more likely than others to develop lung cancer. A risk factor is something that may increase the chance of developing a disease. Studies have shown the following risks factors for lung cancer:
- Smoking Tobacco Products
Smoking is the number one risk factor for developing lung cancer. If you smoke, quit. - Exposure to Environmental Tobacco
Secondhand smoke, comes from the burning end of a cigarette or cigar and the smoke that has been breathed out by a person smoking. Exposure to the product of burning tobacco, includes toxic smoke particles that cling to surrounding clothing, furniture, carpet and the area long after the smoke has cleared. - Exposure to Asbestos
Asbestos is a cancer-causing group of minerals that occurs naturally in the environment as bundles of fibers. If products containing asbestos are disturbed, tiny asbestos fibers are released into the air. If these fibers are breathed in, they can be trapped in the lungs and remain there for a long time causing scarring and irritation. - Exposure to Radon
Radon is a radioactive gas released by the breakdown of uranium in some soils, rocks and water. Radon exposure is the second-leading cause of lung cancer after smoking tobacco products. - Family History
People with a parent, sibling or child with lung cancer have a greater risk of developing lung cancer themselves. - History of Radiation Therapy
Individuals who have received radiation treatment, especially on their chest, have an increased risk of lung cancer.
If you think you may be at risk, talk to your doctor. Your doctor may be able to suggest ways to further reduce your risk and can make recommendations for lung cancer screening.
What are the Symptoms of Lung Cancer?
Early lung cancer may not show any symptoms. Some symptoms that could be present include:
- Constant chest pain
- Cough that does not go away and continues to get worse over time
- Fatigue (tiredness)
- Coughing up blood
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing and hoarseness (strained voice)
- Loss of feeling hungry and losing weight without trying
- Repeated problems with pneumonia or bronchitis
- Neck and face swelling
Lung Cancer Screening Recommendations
The recommended screening test for lung cancer is low-dose computed tomography (also called a low-dose CT scan, or LDCT). In this test, an X-ray machine scans the body and uses low doses of radiation to make detailed pictures of the lungs. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for people who have a history of heavy smoking for 30 years (1-pack per day for 30 years or 2-packs per day for 15 years) and smoke now or have quit within the past 15 years, and are between 55 and 80 years old. Most insurances and Medicare Part B cover LDCT screening test.
To learn more about how to get screened for lung cancer, call the Department of Health at 410-222-6180 or 410-222-6071 (Spanish).
Additional Information
If you smoke, try to quit. Order a FREE Quit Smoking Kit that includes local resources or request one from the Community Education Line at 410-222-7979 or email hdltl@aacounty.org. Include your name and complete address.